Urinary Tract Infection
What Is a Urinary Tract Infection?
A urinary tract infection, or UTI, is an infection in any part of your urinary system, which includes your kidneys, bladder, ureters, and urethra.
If you’re a woman, your chance of getting a urinary tract infection is high. Some experts rank your lifetime risk of getting one as high as 1 in 2, with many women having repeat infections, sometimes for years. About 1 in 10 men will get a UTI in their lifetime.
Here’s how to handle UTIs and how to make it less likely you’ll get one in the first place.
Symptoms of UTIs
The symptoms of a UTI can include:
• A burning feeling when you pee
• A frequent or intense urge to pee, even though little comes out when you do
• Cloudy, dark, bloody, or strange-smelling pee
• Feeling tired or shaky
• Fever or chills (a sign that the infection may have reached your kidneys)
• Pain or pressure in your back or lower abdomen

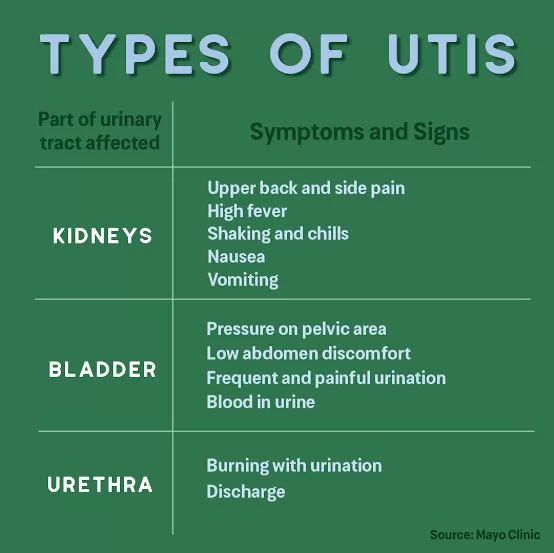
Types of UTIs
An infection can happen in different parts of your urinary tract. Each type has a different name, based on where it is.
• Cystitis(bladder): You might feel like you need to pee a lot, or it might hurt when you pee. You might also have lower belly pain and cloudy or bloody urine.
• Pyelonephritis(kidneys): This can cause fever, chills, nausea, vomiting, and pain in your upper back or side.
• Urethritis(urethra): This can cause a discharge and burning when you pee.
Causes of UTIs
UTIs are a key reason why doctors tell women to wipe from front to back after using the bathroom. The urethra — the tube that takes pee from the bladder to the outside of the body — is close to the anus. Bacteria from the large intestine, such as E. coli, can sometimes get out of your anus and into your urethra. From there, they can travel up to your bladder and, if the infection isn’t treated, can continue on to infect your kidneys. Women have shorter urethras than men. That makes it easier for bacteria to get to their bladders. Having sex can introduce bacteria into your urinary tract, too.
Some women are more likely to get UTIs because of their genes. The shape of their urinary tracts makes others more likely to be infected. Women with diabetes may be at higher risk because their weakened immune systems make them less able to fight off infections. Other conditions that can boost your risk include hormone changes, multiple sclerosis, and anything that affects urine flow, such as kidney stones, a stroke, and a spinal cord injury.
UTI Tests and Diagnosis
If you suspect that you have a urinary tract infection, go to the doctor. You’ll give a urine sample to test for UTI-causing bacteria.
If you get frequent UTIs and your doctor suspects a problem in your urinary tract, they might take a closer look with an ultrasound, a CT scan, or an MRI scan. They might also use a long, flexible tube called a cystoscope to look inside your urethra and bladder.
Treatments for UTIs
If your physician thinks you need them, antibiotics are the most common treatment for urinary tract infections. As always, be sure to take all of your prescribed medicine, even after you start to feel better. Drink lots of water to help flush the bacteria from your body. Your doctor may also give you medication to soothe the pain. You might find a heating pad helpful.
To Watch the Video click here HTTPS://YOUTU.BE/RTKJM7UWLWA











